Is it difficult to keep track of all the tags and analytics codes on your website? Be at ease! The purpose of Google Tag Manager is to enhance both your daily life and your innovative marketing campaigns. You can add tags and collect data for Google Analytics using the free Google Tag Manager tool. Marketers gain access to all previous data because of this third-party tag. Just consider the Facebook advertising.
For the purpose of data collecting for marketers and website owners, this code collects complete information on the number of users who interacted with Facebook advertising. Using the GTM interface, any tag can be inserted.
What is GTM, or Google Tag Manager?
Let’s begin with the fundamentals. We’ll discuss Google Tag Manager’s importance for marketers and offer you a basic introduction to it.Therefore, to save time and effort, see how GTM simplifies the tag implementation procedure and enhances website tracking.
How can I register for Google Tag Manager?
By doing a search for it, logging in with your Gmail ID, and then starting, you can access Google‘s tag manager.
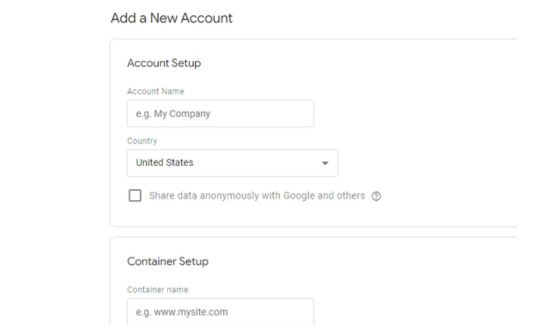
1: Type in your account name. Include the name of your company.If your websites are spread out, you will require numerous accounts for this.
2: Add the name of your country
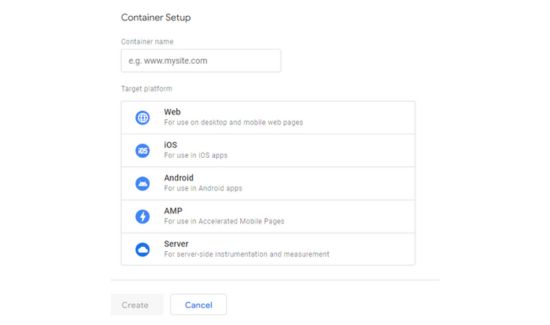
3: Make sure the container name has a link to your website or app.
4: Choose the platform you wish to use, such as Web, iOS, Android, AMP, or Server.

Track Everything You Need by Adding Tags
Learn how tags can help you collect crucial information about user behavior, conversions, and other subjects. Learn how to add several tags, including Google Analytics, Facebook Pixel, and custom event tags, to your website to more properly measure and enhance its performance.
The Use of Variables and Triggers to Customize Your Tracking
Learn about triggers and variables to make your GTM tags better. You will be instructed on how to set exact triggers that only activate tags in response to particular situations. You’ll learn how to accurately recognize moving objects as well as how to use variables to record dynamic data.
Test Your Implementation and Debugging to Ensure a Smooth One
By thoroughly testing and debugging your tags, you can prevent tracking problems and make sure they function as intended. We’ll offer useful hints and tools to ensure a flawless user experience. Additionally, we’ll help you test your tags before posting them online.
Advanced GTM Techniques: Beyond the Data Layer
One innovative technique that provides numerous options for improved tracking and personalisation is the data layer. To get the most of Google Tag Manager, look into custom HTML tags and other helpful tools.
Google Analytics And Google Tag Manager Distinctions
Despite the fact that Google Tag Manager and Google Analytics are both crucial tools for tracking websites and digital marketing, combining the two produces the best results. It’s crucial to comprehend the fundamental distinctions between the two if you want to enhance the performance of your website and obtain valuable data on user activity. Let’s look at how Google Tag Manager and Google Analytics differ from one another.
Functionality
Google Tag Manager (GTM)

A tag management tool like Google Tag Manager (GTM) can simplify the use of tags on your website. Using coding components called tags, it is possible to keep track of pageviews, clicks, form submissions, conversions, and other particular user behaviors and occurrences. The core platform of GTM allows you to add, modify, and remove tags without having to directly touch the website’s source code.
Google Analytics
Google Analytics, a potent online analytics tool, offers comprehensive data and statistics on the performance of your website. It provides useful data on the user base, traffic sources, demographics of the audience, and conversion rates. Google Analytics creates comprehensive reports for review using the information obtained from the GTM tags.
Implementing Tag
Google Tag Manager (GTM)
You only need to add one container tag to your website when utilizing this tag. After the container has been configured, all tracking tags may be added and managed through the GTM interface, negating the requirement for human code implementation.
Google Analytics
A tracking code must be manually introduced to each page of your website in order to use Google Analytics. Even though this tactic is simple, larger websites with many of pages could find it challenging.
Customization and Flexibility
Google Tag Manager (GTM)
GTM provides alternatives for unparalleled personalization and flexibility. It provides precise monitoring and data collecting by allowing you to configure triggers and variables to cause certain tags to fire in response to user activity. In addition, you can design customized tags to meet your particular monitoring needs.
Google Analytics
GTM offers a broader variety of customization choices despite the plethora of pre-built reports and insights. Although there are customized metrics and dimensions available, they need more environment.
Coordination and Application
Google Tag Manager (GTM)
The collaboration of marketers, developers, and other stakeholders is facilitated by GTM. Before deployment, changes to tags can be examined and evaluated, minimizing the possibility of mistakes and ensuring a successful implementation.
Google Analytics
Users who have the necessary permission can regularly access data from Google Analytics. The primary goal of working together is to comprehend the insights and reports provided by the platform.
Conclusion
You’ve now mastered Google Tag Manager, congrats! With the help of this detailed guide, you can successfully integrate and manage tags and make data-driven decisions to improve the functionality of your website. Make use of GTM’s skills to promote your company and improve your digital marketing approach.
Remember that proper monitoring is required to enhance your comprehension of your audience and increase the efficacy of your website. Today, educate yourself about Google Tag Manager to enhance your online visibility. Enjoy your tracking!

